Mock Server
Beside the normal function of a REST API Gateway server, it may play a special role too, in the period of development of the system. A REST API is an interface, where two system components meet, as well as the two teams meet who develop the frontend application from one hand side, and the backend services from the other hand side.
Even in case the two teams are the same, or it is only same individual person, it worth to take into consideration this point, because the parallel development of the components, that are situated at the opposite side of the interface depends on each other. From this perspective the REST API specification can be taken into consideration as a contract, that both parties needs to be conform with. It is not enough to declare the conformance, but that has to be proven too, otherwise the interface will be a kind of Pandora's box, and the bugs occur at any of its sides will be a good reason for the teams for fingerpointing, and to blame each other. in order to avoid this trap, we need a tool that makes possible for both parties to develop independently from the other, and at the same time, helps to prove the conformance with the agreement. This tool is the mock server, which can create a kind of Demilitarized Zone for the cooperating teams.
In order to switch easer to mock server mode, we need to use the --enableMocking or, simply the -mswitch, then the server starts responding to the calls from the REST API model loaded from the OAS files, as you can see on the following Figure:
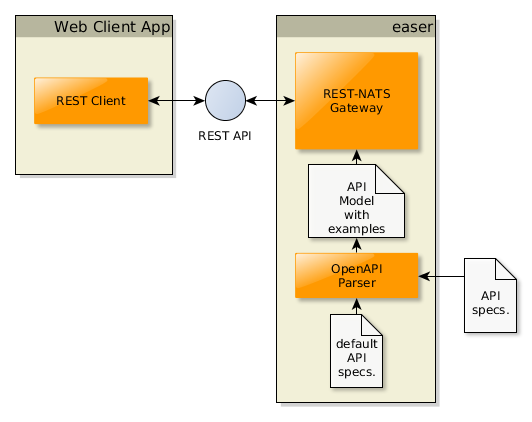
Let's start the easer to act as a static mocking server for the person-rest-api:
$ easer -r person-rest-api/rest-api/api.yml -m
2019-08-05T06:28:57.646Z [easer@4.0.0] info: Load endpoints from /home/tombenke/topics/easer-tutorial/person-rest-api/rest-api/api.yml
2019-08-05T06:28:57.715Z [easer@4.0.0] info: Start up webServer
2019-08-05T06:28:57.728Z [easer@4.0.0] info: Express server listening on port 3007
2019-08-05T06:28:57.729Z [easer@4.0.0] info: App runs the jobs...
2019-08-05T06:29:01.108Z [easer@4.0.0] info: HTTP GET /persons
Then check the endpoints, if they really respond to the requests:
$ curl http://localhost:3007/persons
[{"id":"2a1152ee-4d77-4ff4-a811-598555937625","familyName":"Skywalker","giveName":"Luke"},{"id":"2adce0f1-397f-4923-bdf2-16334a76c29f","familyName":"Skywalker","givenName":"Anakin"}]
$ curl http://localhost:3007/persons/anakin
{"id":"2a1152ee-4d77-4ff4-a811-598555937625","familyName":"Skywalker","givenName":"Luke"}
The responses are coming from the examples defined to the specific endpoint responses. The server takes into consideration of the Accept header, so examples can be defined for multiple mime-types.
There are cases, when the static mocking is not satisfying. We need to implement some intelligence to the mocked service. Another challenge is, when we have implemented some of the backing services, but some of them are not completed, and we need to mock a combination of static and dynamic mocking, as you can see on the next Figure, below:
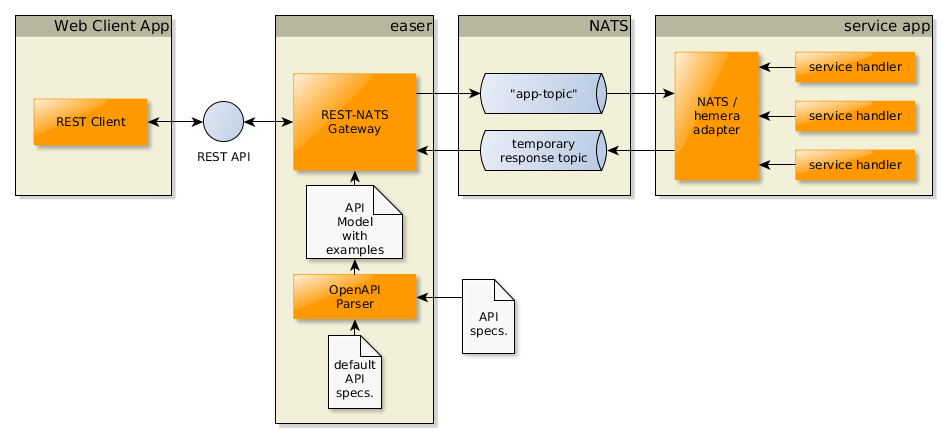
In order to combine the two modes, we need to switch on the NATS middleware and the message forwarding, but at the same time we also can enable the mocking as well:
So lets start the NATS:
$ docker run -it --rm --network=host -p 4222:4222 -p 6222:6222 -p 8222:8222 --name nats-main nats
start, the service implementation:
$ node person-service-js/index.js
and start the easer with mocking and forwarding enabled:
$ easer -r person-rest-api/rest-api/api.yml -n nats://localhost:4222 --topicPrefix person-demo -u -m
Where:
-n nats://localhost:4222: defines the URI of the NATS server;--topicPrefix person-demo: defines the prefix for the name of the topic to use. The topic name is generated by the following pattern:<topicPrefix.<endpoint.method>_<endpoint.uri>;-u: Enableseaserto forward the incoming calls as messages to the NATS topic;-m: Enables the mocking (both static and dynamic as well if MESSAGING forwarding is enabled (-m)).
Now we will see that those endpoints, that has backing service handler, will work:
$ curl http://localhost:3007/persons
[]
$ curl -X PUT http://localhost:3007/persons/leia -H "Content-type: application/json" -d '{"id":"leia","familyName":"Organa","givenName":"Leia"}'
{"id":"leia","familyName":"Organa","givenName":"Leia"}
$ curl http://localhost:3007/persons
[{"id":"leia","familyName":"Organa","givenName":"Leia"}]
What you can see above is that the same as in case of the normal working of REST / NATS gateway mode, which means that the service handlers are responding, however the mocking feature is also switched on. But when will the mocking happen? It happens, if there is an incoming call in relation to an endpoint, that has no registered service handler, but has examples in the swagger descriptor. In such a situation, the easer will detect that the service handler does not respond (ERR {"name":"PatternNotFound","message":"No action found for this pattern"...}) and the NATS connection is timed out, so it finds an example and sends back this static mock data to the client.
In the following example you can see that there is a request to the POST /persons endpoint, that has no registered handler function (it is commented out in the source code), so the static example is sent back:
$ curl -X POST http://localhost:3007/persons
{"id":"2a1152ee-4d77-4ff4-a811-598555937625","familyName":"Skywalker","givenName":"Luke"}