Static Web Server
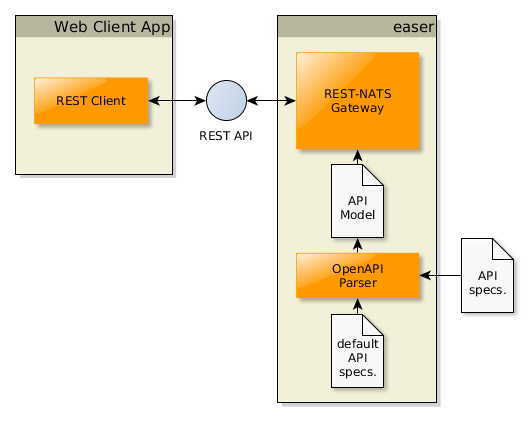
We can define the service endpoints to the easer server via standard endpoint descriptors, as the following Figure shows:
However, in case we do not create endpoint descriptors, neither give it to easer, then the server uses its built-in descriptor, that looks like this:
{
"info": {
"title": "An API that provides the current directory as static content",
"version": "1.0"
},
"paths": {
"/": {
"get": {
"responses": {
"200": {
"description": "OK"
}
},
"x-static": {
"config": {
"dotfiles": "allow",
"index": true
},
"contentPath": "<the-current-working-directory>"
}
}
}
},
"swagger": "2.0"
}
It defines one path that is /, and uses the x-static extensional property to tell the server that this path has to be forwarded to the static-middleware. This property also holds the configuration parameters of this middleware.
So step into a folder (for example the root of the easer repository) that contains the web content you want to observe, then start the server:
$ easer
2019-08-04T13:08:42.398Z [easer@4.0.0] info: Start up webServer
2019-08-04T13:08:42.409Z [easer@4.0.0] info: Express server listening on port 3007
2019-08-04T13:08:42.411Z [easer@4.0.0] info: App runs the jobs...
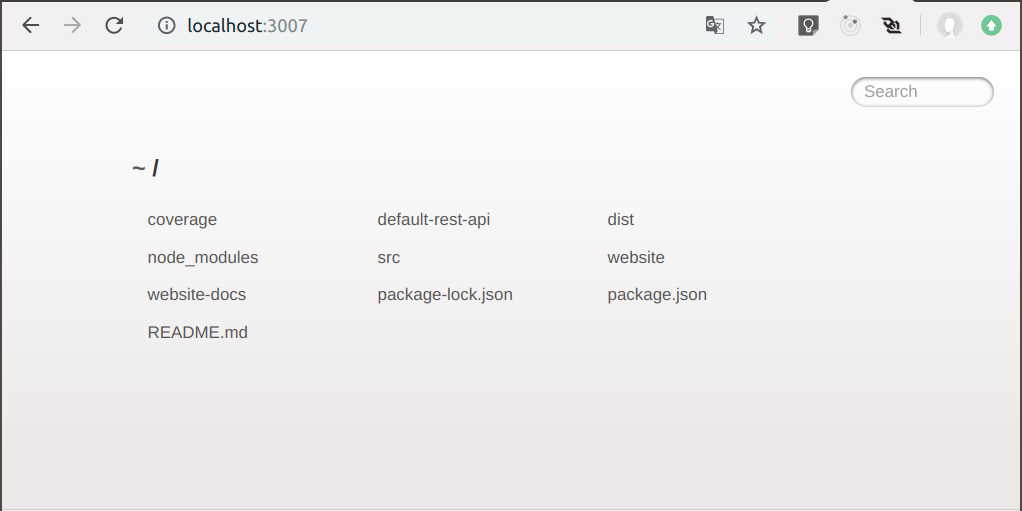
Open the http://localhost:3007/ URL with a browser, then you will something like this: